Compatibility and Software
Device Compatibility Chart
Our cables are compatible with a wide range of medical devices and equipment. Check the chart below to find your device.
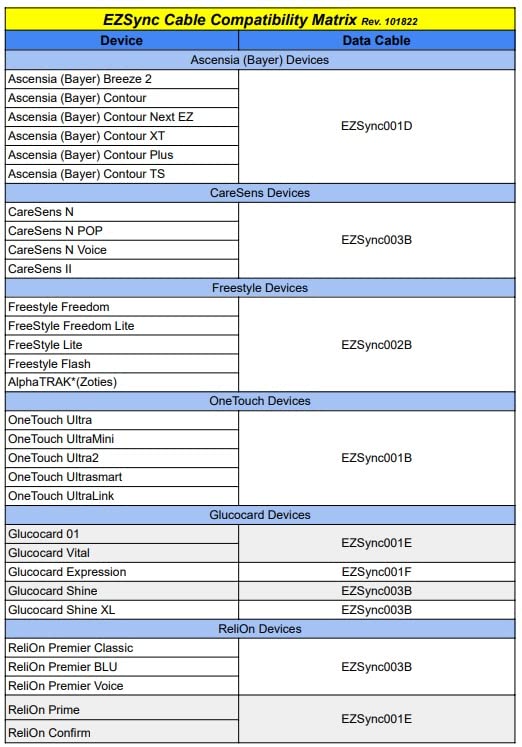
Click on the chart to zoom in
FTDI Drivers
Most of our cables use FTDI USB-to-Serial technology. These drivers are required for Windows and Mac computers to recognize your serial cable or USB adapter.